Leadership Lessons from Lions: Cooperation Over Competition
Leadership in the business world often draws parallels to the animal kingdom, particularly with the image of the male alpha lion, a symbol of power, dominance, and survival of the fittest. However, a deeper examination of lion behavior reveals a more nuanced and arguably more effective model of leadership embodied by female lions. The cooperative strategies of lionesses offer valuable lessons for business leaders, emphasizing the importance of teamwork and collective effort over individual competition.
The Myth of the Alpha Male Lion
The male lion is often seen as the quintessential leader, commanding respect through sheer strength and dominance. This analogy is rooted in the idea of competition as the driving force behind leadership. Male lions compete fiercely to become the alpha, securing territory and mating rights. This survival-of-the-fittest mentality aligns with the traditional view of business leadership, where power and competition are seen as the pathways to success (Schaller, 2018).
However, this perspective overlooks the collaborative nature of true leadership. While male lions are essential for protecting the pride and ensuring its survival, their role is often more symbolic. They maintain dominance through displays of power, but their success is heavily reliant on the cooperative efforts of the pride’s females (Packer, 2020).
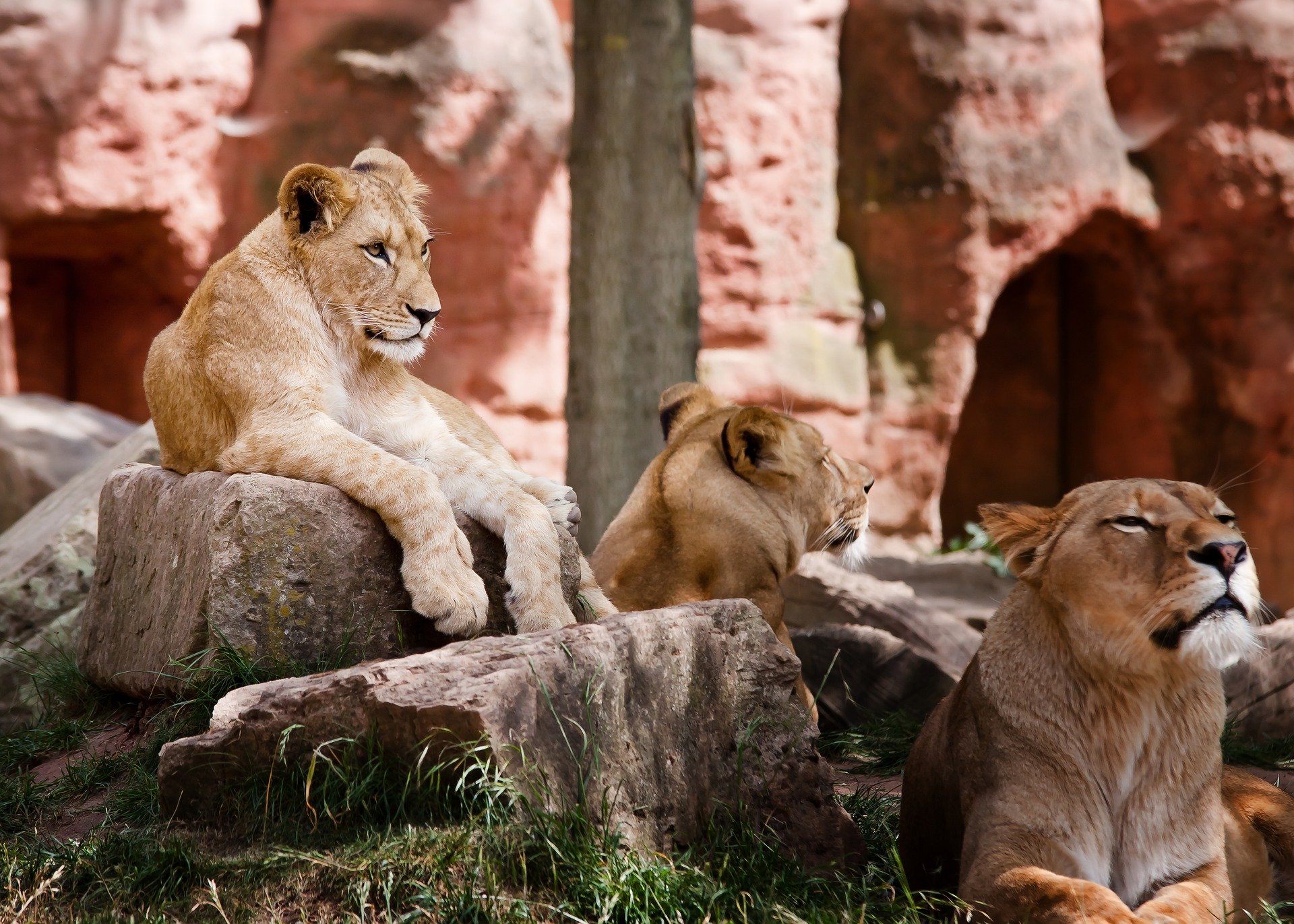
The Power of Cooperation: Lessons from Lionesses
Lionesses, on the other hand, demonstrate the strength of cooperation and teamwork. They are the primary hunters and caretakers within the pride. Their hunting success is not due to individual prowess but rather their ability to work together strategically. Lionesses coordinate their movements, utilize their environment, and rely on each other to bring down prey that is often much larger and faster than themselves (Stander, 1992).
This cooperative hunting model offers a powerful analogy for business leadership. In the corporate world, success often comes from the ability to collaborate effectively, leverage diverse strengths, and work towards a common goal. Just as lionesses depend on each other to ensure the pride’s survival, business leaders must foster a culture of teamwork and mutual support to achieve sustainable success.
The Balance of Power and Cooperation
The dynamic within a lion pride illustrates that effective leadership is not about choosing between competition and cooperation but finding a balance between the two. Male lions provide protection and maintain the pride’s structure, while female lions ensure its day-to-day survival through collaboration. Similarly, business leaders must balance the need for competitive edge with the imperative of fostering a cooperative and inclusive environment (Packer & Heinsohn, 2007).
By embracing the cooperative strategies of lionesses, business leaders can build stronger, more resilient teams. This approach not only enhances performance but also creates a more supportive and innovative work culture. Just as lionesses work together to achieve what they could not accomplish alone, business leaders who prioritize teamwork and collaboration can drive their organizations to new heights of success.
References
Packer, C. (2020). Lions in the Balance: Man-eaters, Manes, and Men with Guns. University of Chicago Press.
Packer, C., & Heinsohn, R. (2007). Ecology and Evolution of Cooperative Breeding in Birds. Cambridge University Press.
Schaller, G. B. (2018). The Serengeti Lion: A Study of Predator-Prey Relations. University of Chicago Press.
Stander, P. E. (1992). Cooperative hunting in lions: the role of the individual. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, 29(6), 445-454.